The Contraceptive Prediction App predicts whether or not a woman in Indonesia is taking Long-term, Short-term, or No contraception. This takes in many features about the woman and her family to enable us to make predictions.
Insights
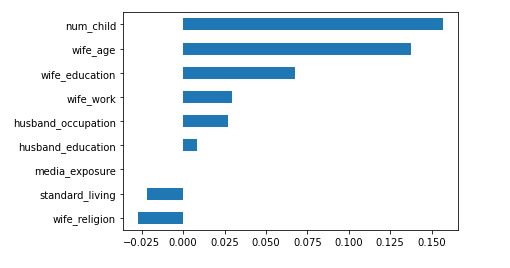
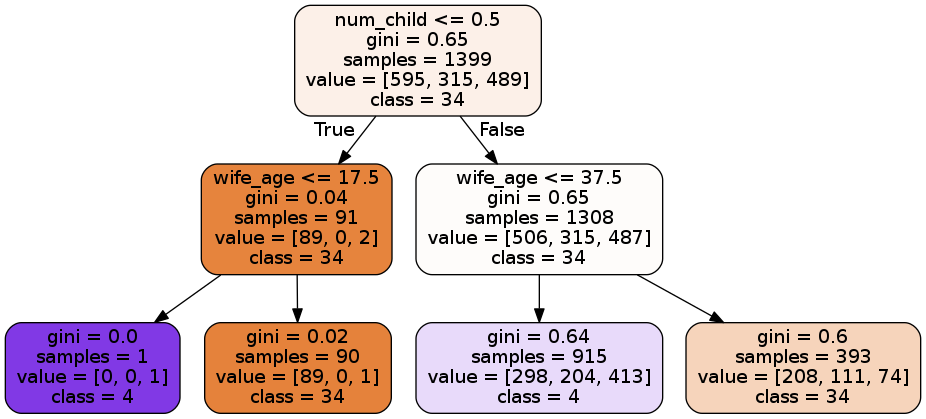
The Baseline Accuracy of Contraception that the model is trying to beat is 42.53%. After training the model we achieved a score of 60.81% accuracy. In addition to this we made a second model to predict the number of children the woman has. I chose this model as a second one because it had the most predictive power in predicting contraception. The baseline accuracy of 18.66%. We were able to increase this to 43.38%. The most influential features in predicting contraception are the age of the woman and the number of children in the family. As you can see by the permutation importance plot below.
Process
I chose the target by looking at what variable was affected most by the other features. This is why I selected contraception as my target. The metric used to evaluate the Random Forest Model was the R2 Score. The baseline score to beat was 42.53%. I Increased the accuracy by 18.28%. I did this by tuning the hyperparameters. I used Random search to conduct a search of the best parameter values over a broad range. Once I narrowed down the best values for the parameters I did a Grid Search to find the best parameter combinations to optimize the model.
This model could be useful in discovering the causes of why a woman in Indonesia is or is not using contraception. This can be useful in various areas of humanitarian work around the world, and not just in Indonesia. The other model is useful for predicting the size of the family based on the contraception used. The Partial Dependence Plot above shows how likely a woman is to not use contraception based on her age and how many children she has.